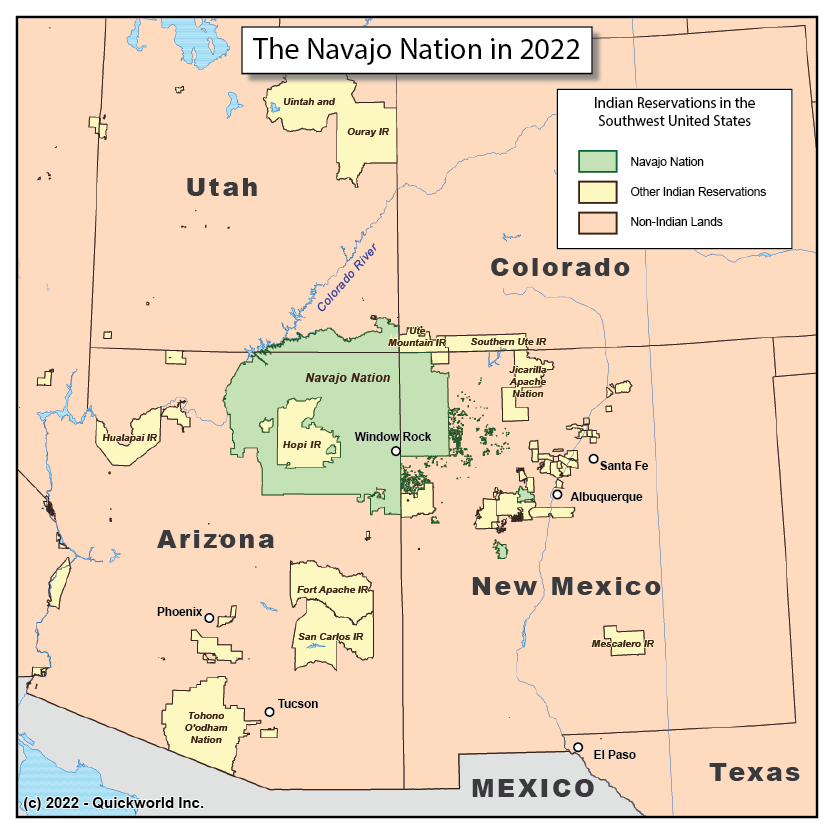
Our Series on Autonomous Territories takes us to the Southwestern United States, home to the Navajo Nation. The Navajos are a tribe of the Na-Déné ethno-linguistic group, which also includes the Apaches, as well as many tribes as far North as Canada.
The Navajo Nation is the largest and most populous of the US Indian Reservations, a series of territories where indigenous nations were granted self-government by the Federal Government. It is also located in an area that mostly overlaps the traditional lands of the Navajos, which is a rare occurrence among Reservations. Its land area covers over 70,000 square km, and it is home to close to 200,000 residents.
While being located partly in the States of Arizona, New Mexico and Utah, the Navajo Nation functions autonomously from those states, and it has its own three branches of government. It is administratively divided into five Agencies (similar to Counties) and chapters, the equivalent of municipalities.
The Nation operates its own schools and college, concurrently with State-operated institutions. While the Navajos have their own language, most residents are primarily English speakers. The Nation strives to revive the language by promoting the use of Navajo language in its educational system.
The Navajo Nation in 2022