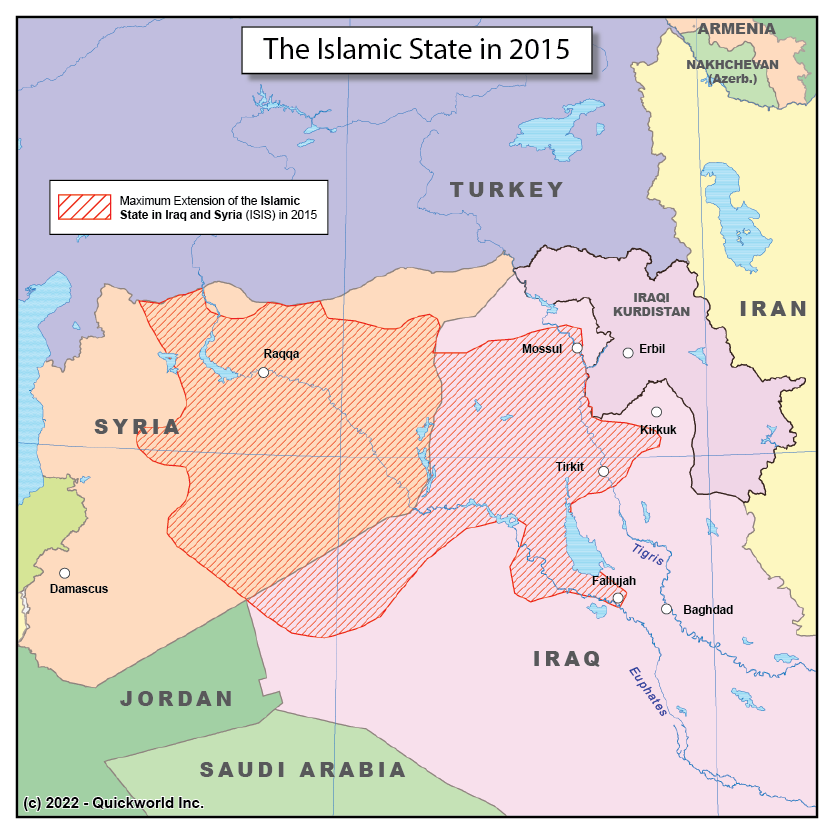
The ISIS insurgency is one of the many conflicts that have rocked the Middle East in modern times. It is different from all others, however, due to its fundamentalist nature and its blunt denial of modern states and international borders.
ISIS stands for the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria, sometimes translated from Arabic as ISIL (IS in Iraq and the Levant). The insurgency started as an uprising in Western Iraq by Sunni Arab populations against the domination of Shia Iraqis who gained power after the American intervention of the early 2000s. Animated by a strong reference to Wahabi Islam, the group gradually controlled most of Western Iraq as the American troops exited from Iraq, and crossed into Eastern Syria by 2014, as that country was descending into a Civil War.
ISIS declared the Caliphate, a theocratic state whose ultimate goal was to govern the entire Muslim World, and were known for their brutality as well as their ability to draw many fighters coming from all over the World, particularly from Western nations. It took an ad hoc coalition comprising all nations who felt threatened by this new form of radicality to reduce their stronghold and eradicate ISIS by 2019.
The ISIS Insurgency